🍏 Healthy Food Habits: Eat to Heal, Not Just to Fill
Healthy food habits are key to overall wellness and sustained energy. A balanced diet helps prevent chronic diseases like diabetes and fatty liver by supporting stable blood sugar and reducing inflammation.
JK Lifestyle follows Dr. Jahangir Kabir’s natural, science-backed approach to promote simple, sustainable eating habits that boost your health for the long term.
✅ The Core Principles of Healthy Eating:
Choose Natural & Organic Foods — Free from chemicals, rich in nutrients.
Balance Macronutrients — Ensure the right intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats.
Nourish with Micronutrients — Vitamins & minerals are essential for overall well-being.
Support Gut Health — Fiber-rich foods aid digestion and detoxification.
Stay Hydrated — Proper hydration improves metabolism and cellular function.
By adopting healthy eating habits, you can:
Manage body weight effectively.
Strengthen your immune system.
Enhance long-term health and disease prevention.
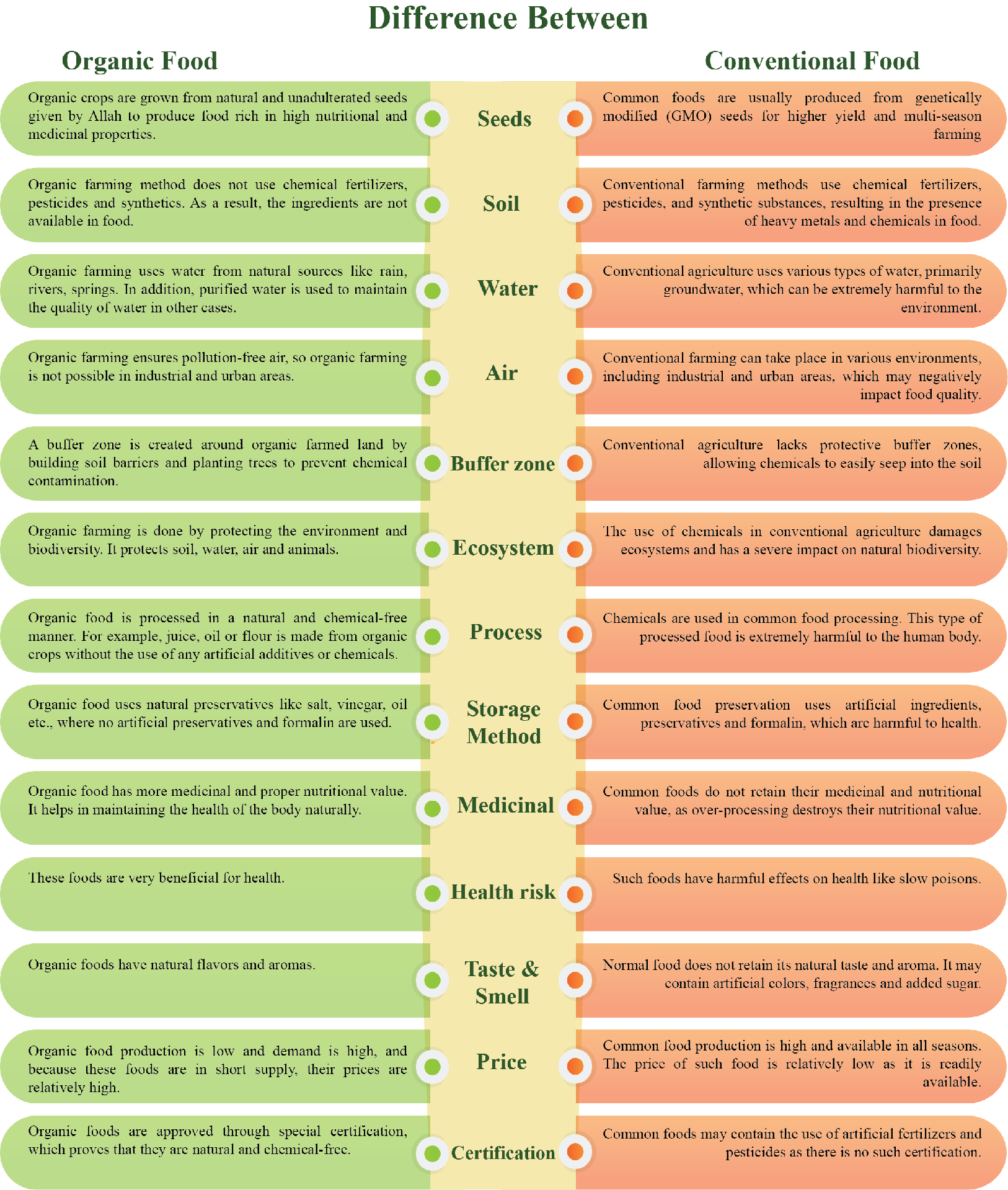
Difference Between Organic Food & Conventional Food
The Importance of Nutrition in a Healthy Diet
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy diet, as it directly supports the body’s growth, energy production, immune system, and overall function. A nutritious diet provides the essential elements our body needs to perform daily activities and maintain physical and mental well-being.
Nutrition is the process through which our body absorbs essential nutrients from food and uses them in various bodily functions. It is essential for maintaining health and ensuring the body functions properly. Nutrition is generally categorized into macronutrients (such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (such as vitamins and minerals).
What Are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients, commonly known as “macros,” are the nutrients we consume in larger quantities. These include carbohydrates, lipids (fats), and proteins. Each macronutrient plays specific roles in the body, such as providing energy to the central nervous system, protecting vital organs, building and maintaining muscles, supporting proper growth and development, and boosting the immune system.
News

Carbohydrate-Rich Foods
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy, easily digestible and providing quick energy. After consumption, carbohydrates are converted into glucose, which is used as fuel for muscles and the brain.
Energy per gram: 4 kcal
Examples: Rice, bread, potatoes, fruits, milk, wheat, or similar grains.

Protein-Rich Foods
Proteins are essential for the development and repair of body tissues and muscles. Once digested, proteins break down into amino acids, which are used for the body’s structural and functional needs.
Energy per gram: 4 kcal
Examples: Fish, meat, lentils, eggs, peas, nuts.

Fat-Rich Foods
Fats help store energy, regulate body temperature, and aid in the absorption of essential vitamins. Fats provide the highest number of calories among nutrients.
Energy per gram: 9 kcal
Examples: Olive oil, coconut oil, avocado, nuts, ghee.
What are Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are nutrients that are required in smaller amounts and include vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals (commonly known as micronutrients). Your body uses vitamins and minerals for various metabolic processes, such as maintaining cellular function, growth, and proper development.
Phytochemicals are chemical compounds produced by plants. While they are not classified as essential nutrients, there is evidence that these compounds may offer health benefits.
Types of Micronutrients:
Vitamins:
Vitamins are organic nutrients that help the body perform a wide range of vital processes. Since the body cannot produce vitamins on its own, they must be obtained from food. Vitamins are categorized into two types:
1. Fat-Soluble Vitamins: These include vitamins A, D, E, and K, which are stored in the body's fat tissues.
2. Water-Soluble Vitamins: These include
vitamin C and B-complex vitamins (like B1, B2, B12), which are not stored in
the body and are excreted through urine if consumed in excess.
Minerals:
Minerals are inorganic elements that are crucial for bones, teeth, blood circulation, and nerve functions. They are divided into two types:
1.Macrominerals: These include calcium, potassium, and magnesium, which the body needs in larger amounts.
2. Microminerals: These include iron, zinc, and copper, required in smaller quantities.
Phytochemicals/Phytonutrients:
Phytonutrients are plant-derived chemical compounds that contribute to a plant's color, aroma, and flavor. These compounds are known to boost the immune system and act as antioxidants. Examples include:
- Carotenoids (found in carrots, tomatoes)
- Flavonoids (found in berries and green tea)
- Sulforaphane (found in broccoli)
Additional Important Nutritional Elements:
Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber aids digestion and prevents constipation. It is found mainly in plant-based foods and comes in two types:
Special Nutritional Foods:

Soluble Fiber:
Dissolves in water and helps control cholesterol and glucose levels.
Examples: chia seeds, basil seeds, guava, citrus fruits.

Insoluble Fiber:
A Helps remove toxins from the body and supports digestive function.
Examples: steel-cut oats, buckwheat, nuts, vegetables, brown rice.
Superfoods:
Superfoods are nutrient-dense foods that offer a wide range of health benefits. They boost immunity, provide energy, and promote long-term health.
Examples: Organic Maca-Cacao Blend, Chia Seeds, Spirulina, and Quinoa Functional Foods:
Functional foods not only provide essential nutrients but also offer specific health benefits beyond regular foods. These foods are often consumed to prevent diseases or improve health conditions.
Examples: Probiotic Yogurt (improves gut health), Vinegar, Turmeric Booster, Huana Ropo Macho, and Flax Seeds.
Including
these foods in your regular diet can improve overall health and boost your
immune system. Below are examples of additional superfoods and functional foods
that you can consider adding to your diet.

Superfoods:
Superfoods are nutrient-dense foods that offer a wide range of health benefits. They boost immunity, provide energy, and promote long-term health.
Examples: Organic Maca-Cacao Blend, Chia Seeds, Spirulina, and Quinoa.

Functional Foods:
Functional foods not only provide essential nutrients but also offer specific health benefits beyond regular foods. These foods are often consumed to prevent diseases or improve health conditions.
Examples: Probiotic Yogurt (improves gut health), Vinegar, Turmeric Booster, Huana Ropo Macho, and Flax Seeds.
List of Super Food and Functional Food
🧠 Conclusion: Eat with Purpose, Heal from Within
Healthy eating isn't just about avoiding illness — it's about fueling your body with purpose. By choosing organic, nutrient-rich, and functional foods, you give your body the tools it needs to detox naturally, support immunity, stabilize energy, and prevent chronic disease.
At JK Lifestyle, inspired by Dr. Jahangir Kabir's science-based nutrition philosophy, we believe food should be your medicine. With the right knowledge and products, you can build lifelong habits that heal — not just fill.

Product highlight
🚀 Ready to Transform Your Eating Habits?
Choose foods that work for your health, not against it.
Explore our curated selection of superfoods and functional nutrition products designed to:
✅ Improve digestion & metabolism
✅ Boost immunity & energy levels
✅ Support weight control & disease prevention
✅ Follow Dr. Jahangir Kabir’s natural health protocol